Basic Grammar
Data type
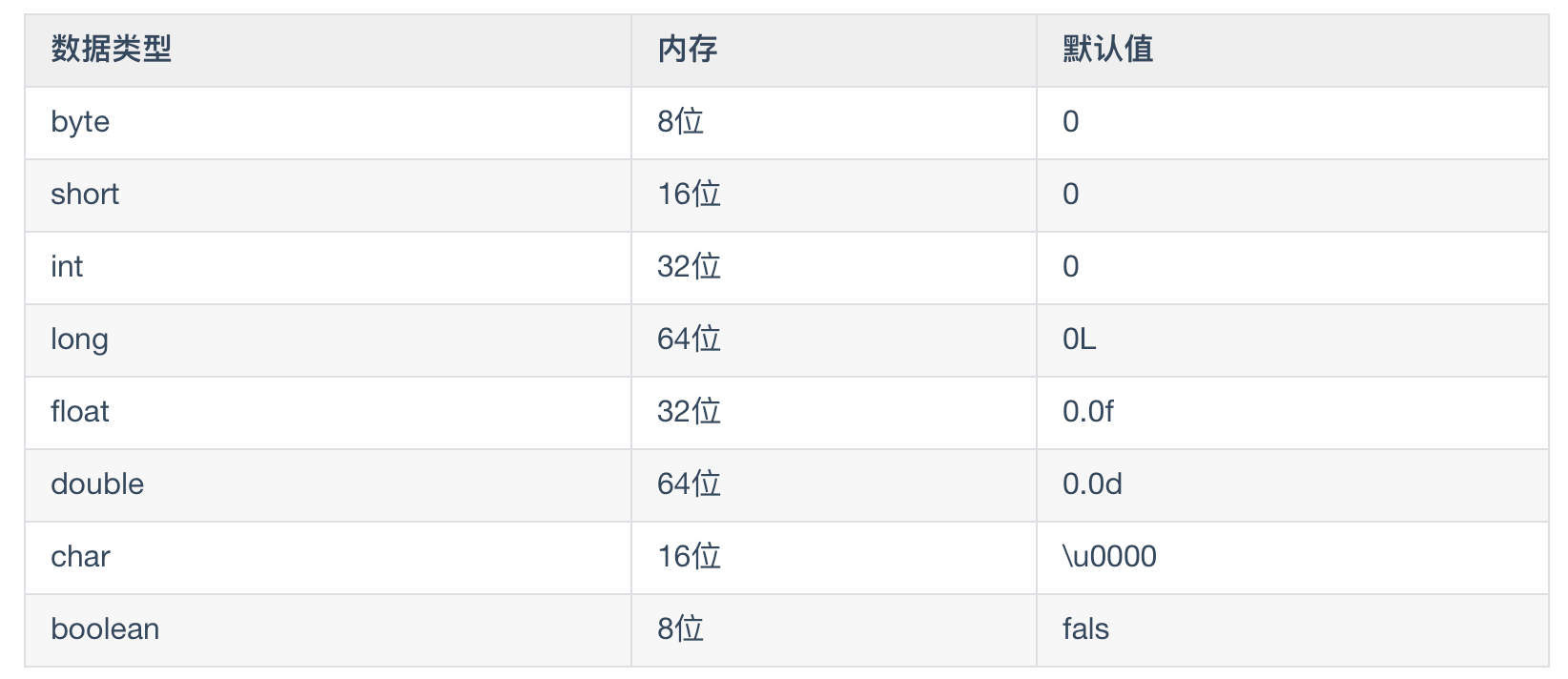
- Integer types: byte, short, int, long
- Floating point types: float, double
- Character type: char
- Boolean: boolean
Java is a case sensitive language, the first letter of classes should be capitalised and package names as much as possible lower case.
Operators
Assignment operators
| operator | description | example |
|---|---|---|
| = | A simple assignment operator that assigns the value of the right operand to the left operand | C = A + B assigns the value obtained by A + B to C |
| + = | The summation operator, which adds the left operand and the right operand to the left operand | C + = A is equivalent to C = C + A |
| - = | The subtraction and assignment operator, which subtracts the left operand from the right operand to assign a value to the left operand | C - = A is equivalent to C = C - A |
| - = | The multiply and assign operator, which multiplies the left operand by the right operand to assign a value to the left operand | C = A is equivalent to C = C A |
| / = | The division and assignment operator, which divides the left operand by the right operand to assign a value to the left operand | C / = A, which is equivalent to C = C / A if C is the same type as A |
| (%) = | The modulo and assignment operator, which takes the left and right operands and assigns them to the left operand | C % = A is equivalent to C = C % A |
| << = | The left shift assignment operator | C << = 2 is equivalent to C = C << 2 |
| >> = | The right shift operator | C >> = 2 is equivalent to C = C >> 2 |
| &= | bitwise and assignment operators | C &= 2 is equivalent to C = C &2 |
| ^ = | The bitwise iso-or assignment operator | C ^ = 2 is equivalent to C = C ^ 2 |
| | = | The bitwise or assignment operator | C | = 2 is equivalent to C = C | 2 |
Arithmetic operators
One thing to note about arithmetic operators is the priority issue. When there are multiple operators in an expression, the order of priority of the operators determines the order of computation, e.g. multiply and divide first, then add and subtract, () has the highest priority.
Self-incrementing, self-subtracting operators
int a = 1;
int b = ++a;
int c = a++;
Comparison operators
! operator
The result of the comparison operator is of the boolean type. If the result of the operator holds, the result of the operation is true, otherwise it is false.
Logical operators
Bitwise operators
The bitwise operator is used to manipulate each bit of an integer base type. The bitwise operator performs a Boolean algebraic operation on the corresponding bit in both arguments and produces a final result. Suppose the value of integer variable A is 60 and the value of variable B is 13.
| Operators | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| & | If the corresponding bits are both 1, the result is 1, otherwise it is 0 | (A & B), giving 12, i.e. 0000 1100 |
| | | If the corresponding bits are both 0, the result is 0, otherwise it is 1 | (A | B) to get 61, i.e. 0011 1101 |
| ^ | If the corresponding bits have the same value, the result is 0, otherwise 1 | (A ^ B) yields 49, i.e. 0011 0001 |
| ~ | The inverse by bit operator flips each bit of the operand, i.e. 0 becomes 1 and 1 becomes 0. | (~A) yields -61, i.e. 1100 0011 |
| << | The bitwise left shift operator. The left operand is shifted bitwise left by the number of bits specified by the right operand. | A << 2 gives 240, i.e. 1111 0000 |
| >> | The bitwise right shift operator. Shifts the left operand by the number of bits specified by the right operand. | A >> 2 gives 15, which is 1111 |
| >>> | The bitwise right shift complementary zero operator. The left operand is shifted to the right by the number of bits specified by the right operand, with the resulting empty bits filled with zeros. | A >>> 2 to get 15 i.e. 0000 1111 |
Ternary operators
The syntax is: conditional expression ? Expression 1: Expression 2, if the result of the conditional expression is true then expression 1 is executed, otherwise expression 2 is executed.
variable x = (expression) ? value if true : value if false
keyword
| category | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access Control | private | protected | public | ||||
| class, method and variable modifiers | abstract | class | extends | final | implements | interface | native |
| new | static | strictfp | synchronized | transient | volatile | ||
| program control | break | continue | return | do | while | if | else |
| for | instanceof | switch | case | default | |||
| error handling | try | catch | throw | throws | finally | ||
| package related | import | package | |||||
| basic type | boolean | byte | char | double | float | int | long |
| short | null | true | false |
| reserved | goto | const | | | | | | |
Comments
public class HelloWorld {
/*
* This is the first Java program
* It will print Hello World
* This is an example of a multi-line comment
*
*/
public static void main(String[] args){
// This is an example of a single line comment
/* This is also a one-line comment example */
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}